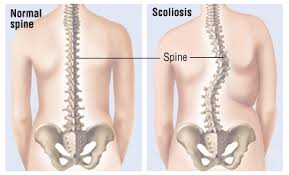
Chronic Pain : back related to body position tilted laterally.
Goal: Pain is reduced or lost.
Interventions:
1. Assess the type, intensity and location of pain.
R /: Helpful in evaluating the pain, define the intervention options, specify the effectiveness of the therapy.
2. Adjust the position that increases the sense of comfort.
R /: Reduce muscle tension and coping adequately.
3. Maintain a quiet environment.
R /: Increase sense of comfort.
4. Teach relaxation and distraction techniques.
R /: To divert attention, thus reducing pain.
5. Encourage postural exercises regularly.
R /: With posturan exercise regularly speed up the process to fix the position of the body.
6. Collaboration: providing analgesic.
R /: To meredahkan pain.
Impaired Physical Mobility related to unbalanced posture.
Goal: Improve the physical mobility.
Interventions:
1. Assess the level of physical mobility.
R /: Influencing choice / monitoring the effectiveness of the intervention.
2. Increase activity if the pain is reduced.
R /: Provide an opportunity to expend energy.
3. Help and teach active joint range of motion exercises.
R /: Increase muscle strength and circulation.
4. Involve the family in performing self-care.
R /: Family cooperative can provide comfort to the patient.
Disturbed Body Image related to posture tilted laterally.
Goal: body image disturbance is resolved.
Interventions:
1. Encourage to express feelings and problems.
R /: Assist in ensuring trouble to start the troubleshooting process.
2. Give an open environment or supporting the patient.
R /: Increase the statement of beliefs / values about positive subjects and identify misconceptions / myths that can affect the assessment of the situation.
3. Discuss the patient's perception about themselves and their relationship to change and how the patient sees himself in the pattern / role functioning normally.
R /: to help define the problem in relation to the previous pattern of life and assist in problem solving.
4. Encourage / provide visits by people who suffer from scoliosis, especially those that have succeeded in rehabilitation.
R /: Friends who have gone through the same experience, acting as role models and can provide validity statement and also hope for recovery and a normal.